8.2 Trends Related to Increased Health Care Costs
The cost of health care in the United States is higher than any other country in the world and has significant economic impact on our economy.[1] U.S. health care spending grew 4.6 percent in 2019, reaching $3.8 trillion or $11,582 per person. Health care spending accounts for 17.7 percent of the nation’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP).[2] See Figure 8.1[3] for a graph of health care cost as a percentage of GDP in the United States compared to other countries around the world.

The increasing costs of health care have several negative impacts on society, employers, and individuals, including the following effects:[4]
- When the government spends more on health care, the national debt increases and funds available for other programs decrease.
- When people spend more on health care, they have less money to spend on other items. When health insurance is paid by their employer, people are paid less.
- When employers spend more on health care, the costs of their products and services increase. Jobs may be moved to countries with lower health care costs.
- An increasing number of people cannot afford health care insurance. When people without health care insurance receive health care, they often cannot pay for it. As a result of unpaid bills, this care is indirectly paid for by other people paying increased insurance premiums and taxes.
- People without health care insurance may not seek preventative care and develop a more costly, serious medical disorder that could have been prevented.
- Medical bills that are not covered by health insurance can cause bankruptcy.
There are several national trends affecting health care costs, including the aging population, increased costs of medical technology, increased prescription medication cost, and the Affordable Care Act.
Aging Population
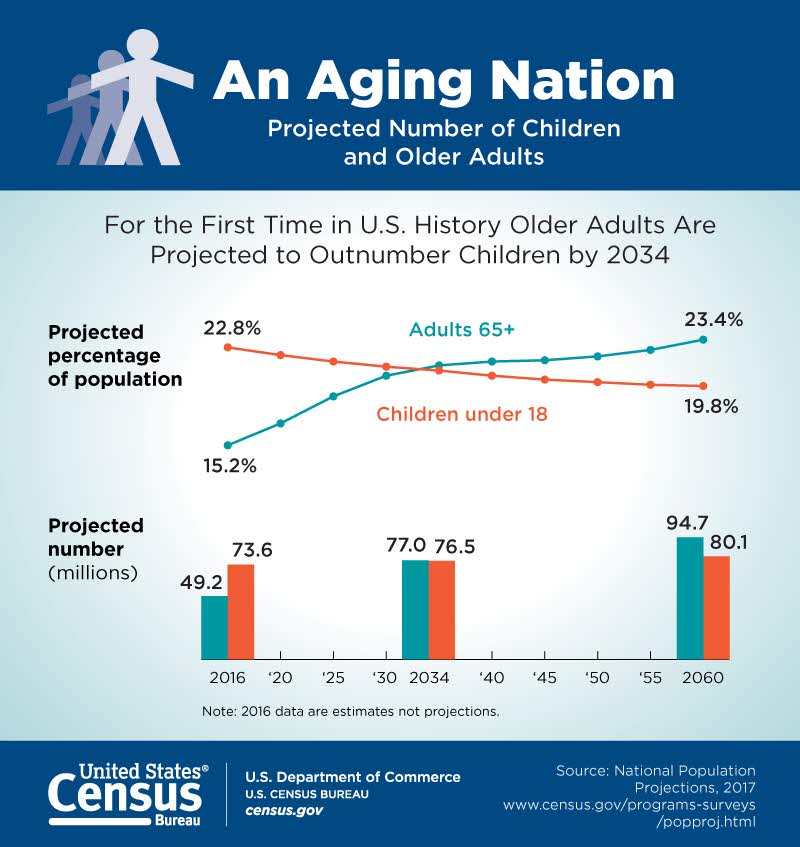
According to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ), the United States has a growing number of older adults (age 65 years or older) who are living longer than previous generations. It is anticipated that older adults will make up more than 20 percent of the U.S. population starting in 2030.[5] See Figure 8.2[6] for an illustration of the aging population from the U.S. Census Bureau. This change in demographics will cause increased national health care costs because older adults experience more chronic conditions than younger populations with increased demand for expensive specialty care.[7]
Increased Costs of Medical Technology
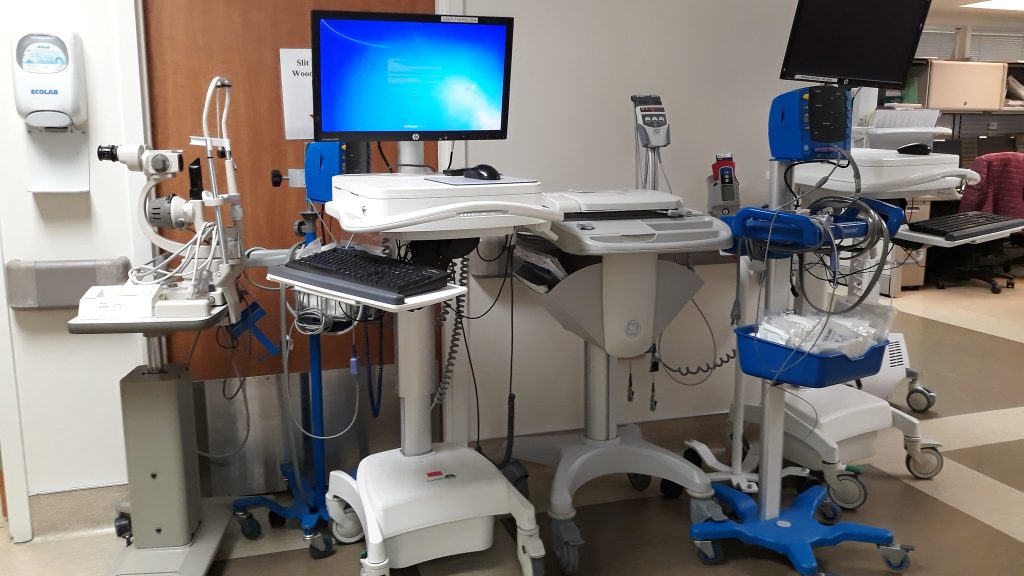
Highly visible medical technology, such as organ transplantation, diagnostic imaging systems, and biotechnology products, attract both praise and blame. Evolving medical technologies may save lives and improve a client’s health status, but they are also viewed as a dominant cause of continued escalation of medical costs. Research suggests that medical technology accounts for about 10 to 40 percent of the increase in health care expenditures over time.[8] See Figure 8.3[9] for an image of common technology used in health care.
Medical technologies, especially new ones, must justify their costs in a climate of competing claims on limited resources. Resource allocation follows American society’s objective of cost effectiveness: if a new technology improves health outcomes at a lower cost than existing technologies, it should be adopted; otherwise, it should not.[10]
Increased Prescription Medication Costs
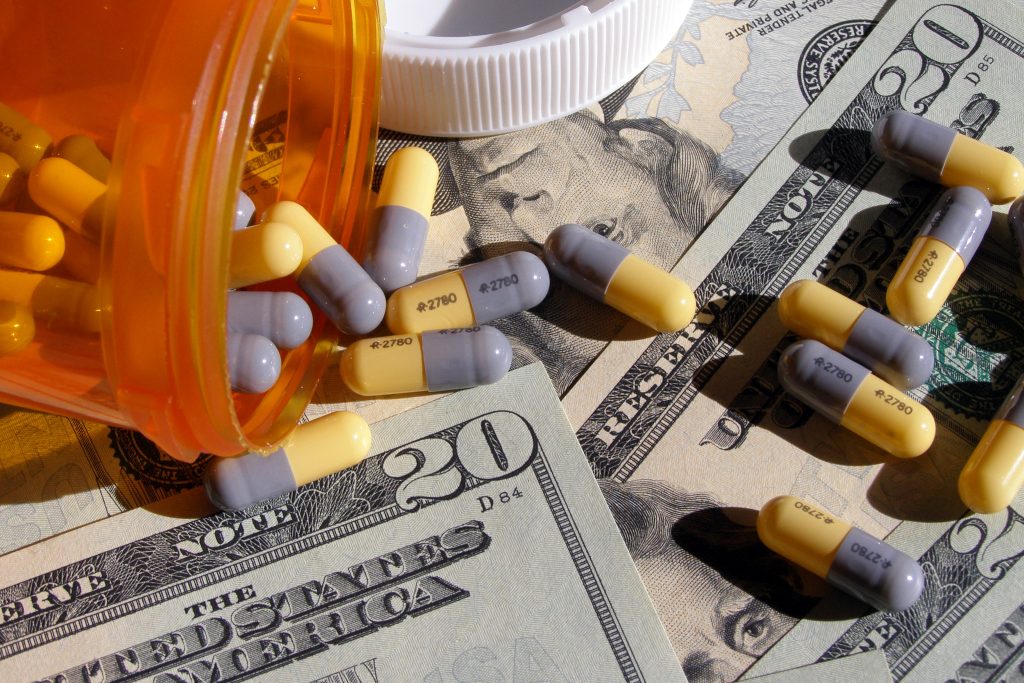
Retail prices for commonly-used prescription medications continue to increase twice as much as inflation, contributing to increased health care costs and making these life-sustaining medicines potentially unaffordable to many Americans. According to a recent AARP Rx Price Watch report, in 2020 prices for 260 commonly used medications increased 2.9 percent while the general rate of inflation was 1.3 percent.[11] For example, Symbicort, a medication used to treat asthma and COPD, increased 46 percent, from $2,940 to $4,282.[12] See Figure 8.4[13] for an illustration of prescription medication costs.
Although the majority of Americans have either public or private insurance that helps them pay for medications, increased medication prices result in higher health insurance premiums and higher taxpayer costs for the Medicare and Medicaid programs. As a result, national organizations like the American Association of Retired Persons (AARP) advocate for national policy changes, such as allowing Medicare to negotiate the prices of prescription medications with drug companies and allowing private insurance plans to have access to those lower prices.[14]
Many consumers find themselves tasked with the difficult decision of purchasing expensive medication or going without prescribed medication and paying for their famillies’ housing and food. Nurses often become involved in case management activities when assisting clients to obtain medications they can afford. Nursing case management activities are discussed later in this chapter.
Affordable Care Act
The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA), also known as the Affordable Care Act (ACA) or Obamacare, was signed into law in 2010. The purpose of this legislation was to increase consumers’ access to health care coverage and protect them from insurance practices that restricted care or significantly increased the cost of care. The ACA mandated health insurance coverage for employers and individuals. Employers were mandated to provide health care coverage based on the number of their employees, and individuals who were not covered through employer insurance plans were mandated to seek coverage through a newly created Marketplace. The Marketplace provides a central, web-based site that offers three standard health insurance coverage levels to facilitate comparison by consumers. Failure to follow these mandates resulted in annual tax penalties to individuals and businesses. As a result of the ACA and associated Medicaid expansion, 32 million people had health care coverage in 2021.[15],[16] See Figure 8.5[17] for an image of the ACA.

Key Provisions of the ACA
The ACA includes the following key provisions:[18]
- Insurers can no longer deny coverage or care for preexisting conditions like diabetes, asthma, and cancer.
- Young adults may remain on their parents’ insurance plans until they are 26 (even if they are married, financially independent, or not living with their parents).
- Health insurance plans cannot place annual or lifetime limits on coverage, except for nonessential exceptions, such as cosmetic procedures.
- Many preventive services must be provided at no cost to consumers, such as:
- Well-child visits, flu shots, and other common vaccines
- Screening tests for blood pressure and diabetes
- Diagnostic screening tests, such mammograms and colonoscopies
- Counseling services related to mental health and substance use
The ACA also provides an avenue for consumers to appeal insurance companies’ denials for care or payment of services and restricts situations in which an insurance carrier may cancel a policy.
Challenges to the ACA
Although the ACA has significantly increased the number of Americans with health insurance coverage, it continues to be debated. Debates focus on increased taxes and some people’s belief that mandated coverage is governmental intrusion on an individual’s rights. The Affordable Care Act has been challenged three times without success in striking it down. In 2012 the U. S. Supreme Court upheld mandated coverage as a constitutional exercise of Congress’ taxing powers because it could be interpreted as an individual’s choice to maintain health insurance or pay a tax. However, in 2017 Congress set the penalty for failing to comply with the mandate at zero dollars after multiple attempts to repeal and replace the ACA. In June 2021 the U.S. Supreme Court rejected a third major challenge regarding the constitutionality of the ACA. In a 7-to-2 decision, the U.S. Supreme Court upheld the ACA based on the judgment that the states who brought forth the case did not prove damage to citizens because the fines for not having health coverage had been eliminated since the original legislation was passed.[19]
What to Expect Next
Given the Supreme Court’s recent decision regarding the ACA, it is expected the current administration will continue to advocate for the ACA and work towards making permanent ACA tax credits. Congress is also actively debating other legislative proposals to reduce health care costs, such as medication pricing reform and expanding Medicare eligibility age and benefits.[20]
- CMS.gov. (2020, December 16). National health expenditure data - historical. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. https://www.cms.gov/Research-Statistics-Data-and-Systems/Statistics-Trends-and-Reports/NationalHealthExpendData/NationalHealthAccountsHistorical ↵
- CMS.gov. (2020, December 16). National health expenditure data - historical. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. https://www.cms.gov/Research-Statistics-Data-and-Systems/Statistics-Trends-and-Reports/NationalHealthExpendData/NationalHealthAccountsHistorical ↵
- “Health_Care_Cost_as_Percentage_of_GDP.png” by Delphi234 is licensed under CC0 1.0 ↵
- Schreck, R. I. (2020, March). Overview of health care financing. Merck Manual Consumer Version. https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/fundamentals/financial-issues-in-health-care/overview-of-health-care-financing ↵
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. (n.d.). Elderly. https://www.ahrq.gov/topics/elderly.html ↵
- “graying-america-aging-nation.jpg” by U.S. Census Bureau is in the Public Domain ↵
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. (n.d.). Elderly. https://www.ahrq.gov/topics/elderly.html ↵
- Neumann, P. J., & Weinstein, M. C. (1991). The diffusion of new technology: Costs and benefits to health care. In Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Technological Innovation in Medicine, Gelijns, A. C., & Halm, E. A. (Eds.). The changing economics of medical technology. National Academies Press. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK234309/ ↵
- “49458105981_fe87fd521c_o.jpg” by Wonderlane is licensed under CC BY 2.0 ↵
- Neumann, P. J., & Weinstein, M. C. (1991). The diffusion of new technology: Costs and benefits to health care. In Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Technological Innovation in Medicine, Gelijns, A. C., & Halm, E. A. (Eds.). The changing economics of medical technology. National Academies Press. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK234309/ ↵
- Bunis, D. (2021, June 7). Prescription drug price increases continue to outpace inflation. AARP. https://www.aarp.org/politics-society/advocacy/info-2021/prescription-price-increase-report.html ↵
- Bunis, D. (2021, June 7). Prescription drug price increases continue to outpace inflation. AARP. https://www.aarp.org/politics-society/advocacy/info-2021/prescription-price-increase-report.html ↵
- “8265405611_c0f957ebbf_o.jpg” by Chris Potter is licensed under CC BY 2.0 ↵
- Bunis, D. (2021, June 7). Prescription drug price increases continue to outpace inflation. AARP. https://www.aarp.org/politics-society/advocacy/info-2021/prescription-price-increase-report.html ↵
- HealthCare.gov. Insurance marketplace. https://www.healthcare.gov/subscribe/?gclid=Cj0KCQjwiqWHBhD2ARIsAPCDzamNRkS3URx_uUvJGdpX15DrZnVbBadXbPmOjBBlLyjtZBn7cLei6WEaAl8GEALw_wcB&gclsrc=aw.ds ↵
- HHS.gov. About the Affordable Care Act. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. https://www.hhs.gov/healthcare/about-the-aca/index.html ↵
- “The_Affordable_Care_Act.png” by Careilly5801 is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0 ↵
- HHS.gov. About the Affordable Care Act. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. https://www.hhs.gov/healthcare/about-the-aca/index.html ↵
- K&L Gates LLP, Carnevale, A., Hamscho, V., Lawless, T., & Sha Page, K. (2021, June 21). The Affordable Care Act survives Supreme Court challenge: What happens next? JD Supra. https://www.jdsupra.com/legalnews/the-affordable-care-act-survives-3115372/ ↵
- K&L Gates LLP, Carnevale, A., Hamscho, V., Lawless, T., & Sha Page, K. (2021, June 21). The Affordable Care Act survives Supreme Court challenge: What happens next? JD Supra. https://www.jdsupra.com/legalnews/the-affordable-care-act-survives-3115372/ ↵

